Reduction Compasses
From Inventions
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
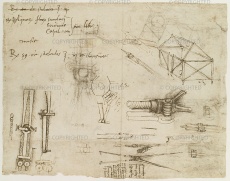
Image: 0101-39792.jpg | Leonardo da Vinci. ''Il Codice Atlantico di Leonardo da Vinci : edizione in facsimile dopo il restauro dell'originale conservato nella Biblioteca Ambrosiana di Milano''. Firenze, 1973-1975, c. 1046r.<br /> | Image: 0101-39792.jpg | Leonardo da Vinci. ''Il Codice Atlantico di Leonardo da Vinci : edizione in facsimile dopo il restauro dell'originale conservato nella Biblioteca Ambrosiana di Milano''. Firenze, 1973-1975, c. 1046r.<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
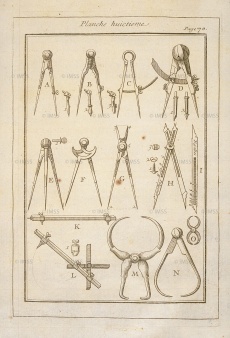
Image: 8528_3202_1659-024.jpg | Nicolas Bion. ''Traité de la construction et des principaux usages des instruments de mathematique'', Paris, 1725, tav. 8.<br /> | Image: 8528_3202_1659-024.jpg | Nicolas Bion. ''Traité de la construction et des principaux usages des instruments de mathematique'', Paris, 1725, tav. 8.<br /> | ||
Revision as of 08:36, 26 July 2010
Name currently used for the compass with intersecting legs, or four-point compasses.
Contents |
Historic Period
1st C. B.C.?
Description
Instrument used exclusively to reproduce drawings in reduced or enlarged scale, having two legs intersecting at a fixed or mobile centre whose opposed points form simple ratios of 1:2, 1:3 or other (Vocabolario della Crusca, 1878). The most ancient was found in the archaeological excavations of Pompeii. In the Renaissance it was known as double compasses, compasso a centro mobile (compass with mobile centre) (Giacomo Contarini) or compasso con le punte doppie (compass with double points) (Muzio Oddi, Fabbrica et uso del compasso polimetro, Milan 1633, Introduction), while in modern terminology it is also called four-point compasses.
Bibliographical Resources
Contarini, Giacomo. Figure d'Istromenti Matematici e loro uso, ms, ca. 1590, Oxford, Bodleian Library, Ms. Canon. Ital. 145, c. 21.
Oddi, Muzio. Fabbrica et uso del compasso polimetro, Milano 1633.
Existing Instruments
Florence, Museo Galileo. Institute and Museum of the History of Science, Inv. 3686.
Florence, Museo Galileo. Institute and Museum of the History of Science, Inv. 655.
Florence, Museo Galileo. Institute and Museum of the History of Science, Inv. 633.
Napoli, Museo Archeologico Nazionale, Inv. 76684
Images
Author of the entry: Filippo Camerota