Monicometer
From Inventions
(Created page with '{{Template invention |nome= Name coined by the inventor combining the Greek words monimos (that which remains immobile) and metron (measure). |inventore= Francesco Pifferi |d…') |
|||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
|link= | |link= | ||
| - | |immagini= <gallery widths=230 heights=368 perrow=3> | + | |immagini= <gallery widths=230 heights=368 perrow=3 > |
Image: 8528_3202_1738-043.jpg | Francesco Pifferi, ''Monicometro instromento da misurar con la vista stando fermo'', Luca Bonetti, Siena, 1595, p. 16.<br /> | Image: 8528_3202_1738-043.jpg | Francesco Pifferi, ''Monicometro instromento da misurar con la vista stando fermo'', Luca Bonetti, Siena, 1595, p. 16.<br /> | ||
Revision as of 09:11, 16 July 2010
Name coined by the inventor combining the Greek words monimos (that which remains immobile) and metron (measure).
Contents |
Inventor
Francesco Pifferi
Historic Period
1595
Description
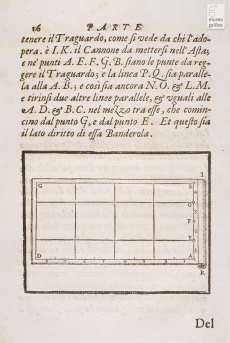
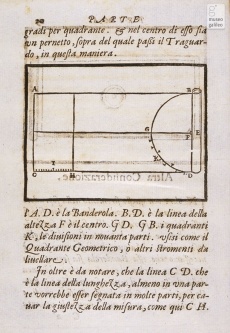
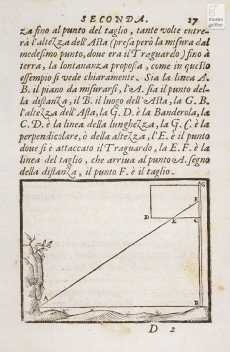
Instrument for architectural measurements and surveying formed of a simple board with sheets of drawing paper on which the surveyor traced the sighted lines directly, constructing one by one the various triangles needed for calculating proportionally the estimated distances. A similar board was described already in the thirteenth century by Domenico da Chivasso, but the device is called by this name only in the treatise of Francesco Pifferi from Siena.
Bibliographical Resources
Domenico da Chivasso, Practica geometriae, ms., XIV secolo, Bibl. Laurenziana, San Marco 215, cc. 124v-144r.
Busard, H.L.L., ed., The Practica Geometriae of Dominicus de Clavasio (Cod. lat. Monac. 410), in «Archive for the history of exact sciences», 2, 1965, 6, pp. 520-575.
Pifferi, Francesco, Monicometro instromento da misurar con la vista stando fermo, Luca Bonetti, Siena, 1595.
Images
Author of the entry: Filippo Camerota