Florentine Archimeter
From Inventions
| (8 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|nome= | |nome= | ||
| - | + | Name adopted by Ostilio Ricci and widely used by sixteenth-century Florentine topographers. The instrument differs however, but only in shape, from the [[archimeter]] of Giovanni Battista Aleotti. | |
| + | |||
| + | |descrizione= | ||
| + | Instrument described by Ostilio Ricci (1590) but probably already in use among Florentine military architects. Its prototype may be seen in the [["Gran Regola" (Great-Rule) of Ptolemy]], from the Medicean instrument collection (A. Santucci, 1593, fol. 45v). Although resembling Leonardo’s [[folding square]], its features are typical of more recent measurement instruments. The archimetro is shaped like a folding square with graduated arms, but has a compass inserted in the joint and a third cross-arm, as in [[Astronomical Staffs |astronomical staffs]]. In addition to measuring inaccessible quantities, the archimetro was used for surveying territories, allowing topographical maps to be compiled immediately, as with the distantiometer, the [[holometer]] and the [[gnomon]]. The same name had been used some years earlier by Giovanni Battista Aleotti, known as Argenta, for a surveying instrument of his invention (see [[archimeter]]). | ||
| - | |||
|inventore= Ostilio Ricci (1540-1603) | |inventore= Ostilio Ricci (1540-1603) | ||
| Line 22: | Line 24: | ||
|strumentiesistenti= | |strumentiesistenti= | ||
| - | [http:// | + | [http://catalogue.museogalileo.it/object/TriangulationCompass.html Florence, Museo Galileo. Institute and Museum of the History of Science, Inv. 645.]<br /> |
| + | [http://catalogo.museogalileo.it/oggetto/Archimetro.html Florence, Museo Galileo. Institute and Museum of the History of Science, Inv. 629.]<br /> | ||
|link= | |link= | ||
| + | http://www.fondazionegalileogalilei.it/museo/collezioni/calcolatori/compassi/schede_compassi/app_ita.html (Italian)<br> | ||
| + | http://www.springerlink.com/content/q56w35403g23j231/ (English) | ||
|immagini= <gallery widths=230 heights=368 perrow=3> | |immagini= <gallery widths=230 heights=368 perrow=3> | ||
| - | |||
Image: AF0026-51566.jpg|Ostilio Ricci, ''Problemi di geometria pratica. L'uso dell'archimetro'', 1590, Firenze, Biblioteca Nazionale Centrale, II-57, c. 37r | Image: AF0026-51566.jpg|Ostilio Ricci, ''Problemi di geometria pratica. L'uso dell'archimetro'', 1590, Firenze, Biblioteca Nazionale Centrale, II-57, c. 37r | ||
| Line 33: | Line 37: | ||
Image: AF0026-51592.jpg|Giorgio Vasari il Giovane, ''Raccolto di varij instrumenti per misurare con la vista'', 1600, Firenze, Biblioteca Riccardiana, ms. Ricc. 2138, c. 76 | Image: AF0026-51592.jpg|Giorgio Vasari il Giovane, ''Raccolto di varij instrumenti per misurare con la vista'', 1600, Firenze, Biblioteca Riccardiana, ms. Ricc. 2138, c. 76 | ||
| - | Image: 0102-41822.jpg|Giulio Parigi, | + | Image: 0102-41822.jpg|Giulio Parigi, of the Stanzino delle Matematiche (Mathematics Room), Florence, Galleria degli Uffizi, detail of the archimeter |
| - | + | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Current revision as of 10:44, 7 September 2010
Name adopted by Ostilio Ricci and widely used by sixteenth-century Florentine topographers. The instrument differs however, but only in shape, from the archimeter of Giovanni Battista Aleotti.
Contents |
Inventor
Ostilio Ricci (1540-1603)
Historic Period
1590
Description
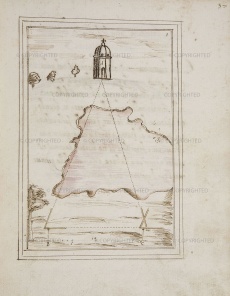
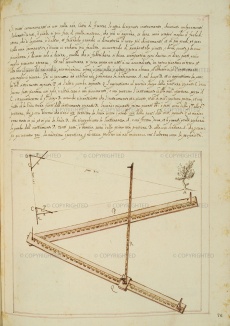
Instrument described by Ostilio Ricci (1590) but probably already in use among Florentine military architects. Its prototype may be seen in the "Gran Regola" (Great-Rule) of Ptolemy, from the Medicean instrument collection (A. Santucci, 1593, fol. 45v). Although resembling Leonardo’s folding square, its features are typical of more recent measurement instruments. The archimetro is shaped like a folding square with graduated arms, but has a compass inserted in the joint and a third cross-arm, as in astronomical staffs. In addition to measuring inaccessible quantities, the archimetro was used for surveying territories, allowing topographical maps to be compiled immediately, as with the distantiometer, the holometer and the gnomon. The same name had been used some years earlier by Giovanni Battista Aleotti, known as Argenta, for a surveying instrument of his invention (see archimeter).
Bibliographical Resources
Ricci, Ostilio. L'uso dell'archimetro di Ostilio Ricci da Fermo mathematico del s. g. duca di Toscana (1590). Firenze, Biblioteca Riccardiana, ms. 2899.
Ricci, Ostilio. Problemi di geometria pratica. L'uso dell'archimetro, 1590. Firenze, Biblioteca Nazionale Centrale, II-57.
Santucci, Antonio. Trattato di diversi istrumenti matematici che si conservano al presente nella Guardaroba del Gran Duca di Toschana presi in disegno in questo libbro, con le loro operazioni come in misurare le lunghezze, largezze, altezze overo profondita, così delle cose terrene come celesti, similmente in levar le piante delle provincie o di qual si voglia cosa con ogni particolarità che giustamente stien ne luoghi loro (1593). Firenze, Biblioteca Marucelliana, ms. C 82, c. 45v.
Vinci, Federico. Ostilio Ricci da Fermo maestro di Galileo Galilei". Fermo, Tip. S. Properzi, 1929.
Existing Instruments
Florence, Museo Galileo. Institute and Museum of the History of Science, Inv. 645.
Florence, Museo Galileo. Institute and Museum of the History of Science, Inv. 629.
Links (External)
http://www.fondazionegalileogalilei.it/museo/collezioni/calcolatori/compassi/schede_compassi/app_ita.html (Italian)
http://www.springerlink.com/content/q56w35403g23j231/ (English)
Images
Author of the entry: Filippo Camerota